
NGINX has become one of the most popular web servers in the world, widely praised for its speed, scalability, and versatility. Originally developed to solve the C10k problem (handling 10,000 simultaneous connections), it has evolved into a multi-purpose tool for web hosting, load balancing, reverse proxying, API gateway management, and even email proxying.
In this article, we’ll cover what NGINX is and what it’s used for. We’ll also dive deep into practical configurations and use cases, including Kubernetes, Docker, reverse proxy setups, HTTPS enablement, and advanced features like embedded keys and domain translation.
What is NGINX?
NGINX is an open-source, high-performance HTTP server, reverse proxy, and load balancer. Unlike traditional servers like Apache, NGINX uses an event-driven, asynchronous architecture that allows it to handle thousands of connections with minimal memory usage.
Key advantages over Apache:
- Better performance for static content.
- Lower memory footprint.
- Event-driven connection handling.
Common use cases include:
- Serving static files.
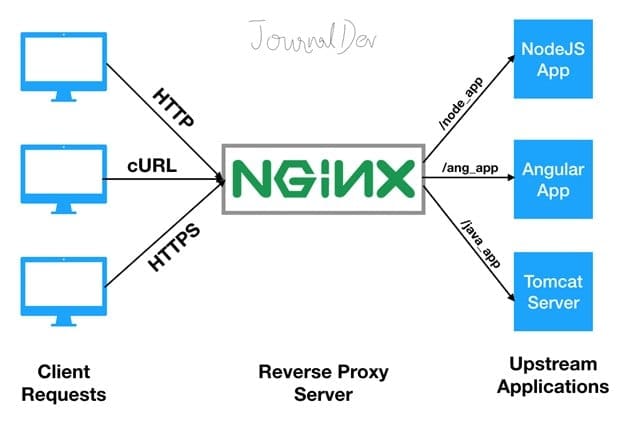
- Acting as a reverse proxy to backend applications.
- Load balancing multiple servers.
- Terminating SSL/TLS connections.
- Handling WebSocket connections.
NGINX Configuration Locations
Where is nginx config in a Kubernetes pod?
If you are running NGINX inside Kubernetes, you can check the configuration inside the container by executing the following command:
kubectl exec -it — cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Or, if you use NGINX Ingress Controller, use this command:
kubectl describe configmap nginx-configuration -n ingress-nginx
On traditional systems, the configuration is usually found at:
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
/etc/nginx/conf.d/
Common NGINX Troubleshooting
How can I fix 404 Not Found NGINX error message?
A 404 error in NGINX usually means the server couldn’t find the requested file. To fix this issue, do the following steps:
- Check the root or alias directive in your location block.
- Verify file permissions.
- Reload NGINX after changes with the following command: sudo nginx -s reload
How do I restart my NGINX server on a MacBook?
Use the following commands for the following installation procedures.
If installed via Homebrew: brew services restart nginx
Or manually: sudo nginx -s reload
NGINX with Docker
Do the following steps for each NGINX with Docker procedure.
How to create NGINX proxy in Docker:
docker run –name nginx-proxy -p 80:80 -v /path/to/conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d -d nginx
How to set up Docker reverse proxy server:
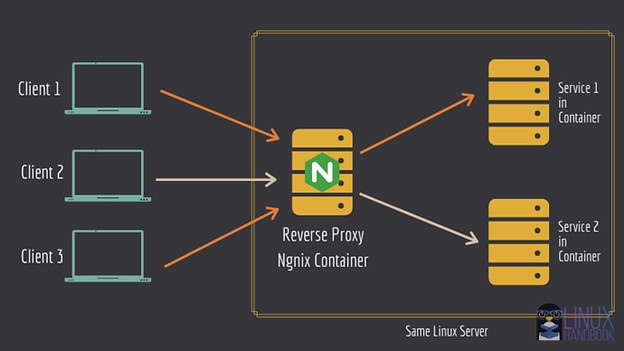
You can point NGINX to backend containers by linking services or using Docker networks.
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend_app:5000;
}
}
NGINX latest Docker image zip can be pulled with:
docker pull nginx:latest
Security & SSL
Do the following steps for each Security and SSL procedure.
How to translate IP to secured domain in NGINX:
Use a server_name directive with SSL certificates:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name example.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/cert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/key.pem;
}
How to enable HTTPS in NGINX:
- Install SSL certificate (Let’s Encrypt, etc.).
- Update your configuration with listen 443 ssl;.
- Reload NGINX.
How to use a password with NGINX .pem and .key:
- Use OpenSSL to remove the password from the private key for automated restarts: openssl rsa -in private.pem -out nopass.key
- Then configure NGINX to use nopass.key.
How to use embedded keys with NGINX:
Embed both certificate and key in the same PEM file and reference it in the ssl_certificate directive.
Using NGINX in Kubernetes (Ingress)
Ingress NGINX is a Kubernetes controller that exposes HTTP/HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within.
Below is an example manifest:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example-ingress
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
– host: example.com
http:
paths:
– path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: my-service
port:
number: 80
NGINX vs Apache
While Apache is process-based, NGINX is event-based, leading to better scalability under heavy loads. Apache excels in .htaccess flexibility and dynamic content handling, while NGINX dominates in static file delivery and high-concurrency scenarios.
Logs & Monitoring
NGINX Logs:
Default locations:
/var/log/nginx/access.log
/var/log/nginx/error.log
These logs help debug issues such as failed requests, SSL handshake errors, or proxy failures.
NGINX Proxy Manager provides a GUI to manage proxies, SSL, and routing rules without editing config files manually.
Advanced Features
- NGINX conf.d http — add custom HTTP server blocks in /etc/nginx/conf.d.
- NGINX include subdomains — use server_name *.example.com;
- APISIX NGINX worker — Apache APISIX uses NGINX workers for plugin execution.
- FileCloud NGINX — integrate FileCloud’s storage gateway with NGINX as a reverse proxy.
- WebSocket NGINX manager — configure proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; for WebSockets.
- Superset config NGINX — proxy Apache Superset through NGINX for HTTPS access.
Installing NGINX and Setting up SSL on Ubuntu
Use the following commands for each procedure of installing NGINX on Ubuntu:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx
sudo certbot –nginx -d example.com
The command above will install NGINX, request an SSL certificate, and configure HTTPS automatically.
Ubuntu install NGINX specific path:
You can use –prefix when compiling from source:
. /Configure –prefix=/opt/nginx make && sudo make install
Restarting and Reloading NGINX
Use the following commands for each Restart and Reload procedures.
- Restart: sudo systemctl restart nginx
- Reload without downtime: sudo nginx -s reload
Conclusion
NGINX is more than a web server — it’s a robust, flexible, and high-performance reverse proxy, load balancer, and API gateway. Whether you’re deploying in Kubernetes, running in Docker, or hosting traditional web applications, its efficiency and scalability make it a top choice.
Its versatility extends from simple static file serving to complex SSL setups, embedded key management, password-protected certificates, and advanced Kubernetes ingress routing. By understanding where configurations live, how to troubleshoot common issues, and how to set up secure, high-performance environments, you can leverage NGINX to its fullest potential.
References:
- NGINX Official Docs
- NGINX Admin Guide
- Kubernetes NGINX Ingress Controller
- Nginx – Wikipedia
- This Russian Software Is Taking Over the Internet | WIRED
- Comprehensive Guide to Nginx: From Basic Setup to Production-Ready Load Balancing | by Sanath Shetty | Jul, 2025 | Medium
- What Is NGINX and What Is It Used For?
- github.com/nginx/kubernetes-ingress/issues/1675?utm_source=chatgpt.com?utm_source=chatgpt.com
- Understanding NGINX: Architecture, Configuration & Alternatives | Solo.io